How to Select DC Coupling & AC Coupling in Solar Energy Storage System?
Feb 06, 2026Against the backdrop of today's energy transition, photovoltaic energy storage systems are becoming a vital component of sustainable energy development due to their unique advantages. The coupling method of solar and storage serves as the pivotal link in achieving efficient energy utilization.
Today, Sailsolar will help you explore a crucial concept between two coupling architectures in solar power system: DC coupling and AC coupling in solar-storage systems.The key to understanding these two architectures lies in identifying where the energy from photovoltaics and the storage battery converges.
DC coupling: Circuit of PV and the storage battery converge on the DC side.
AC coupling: Circuit of PV and storage battery will converge on the AC side.
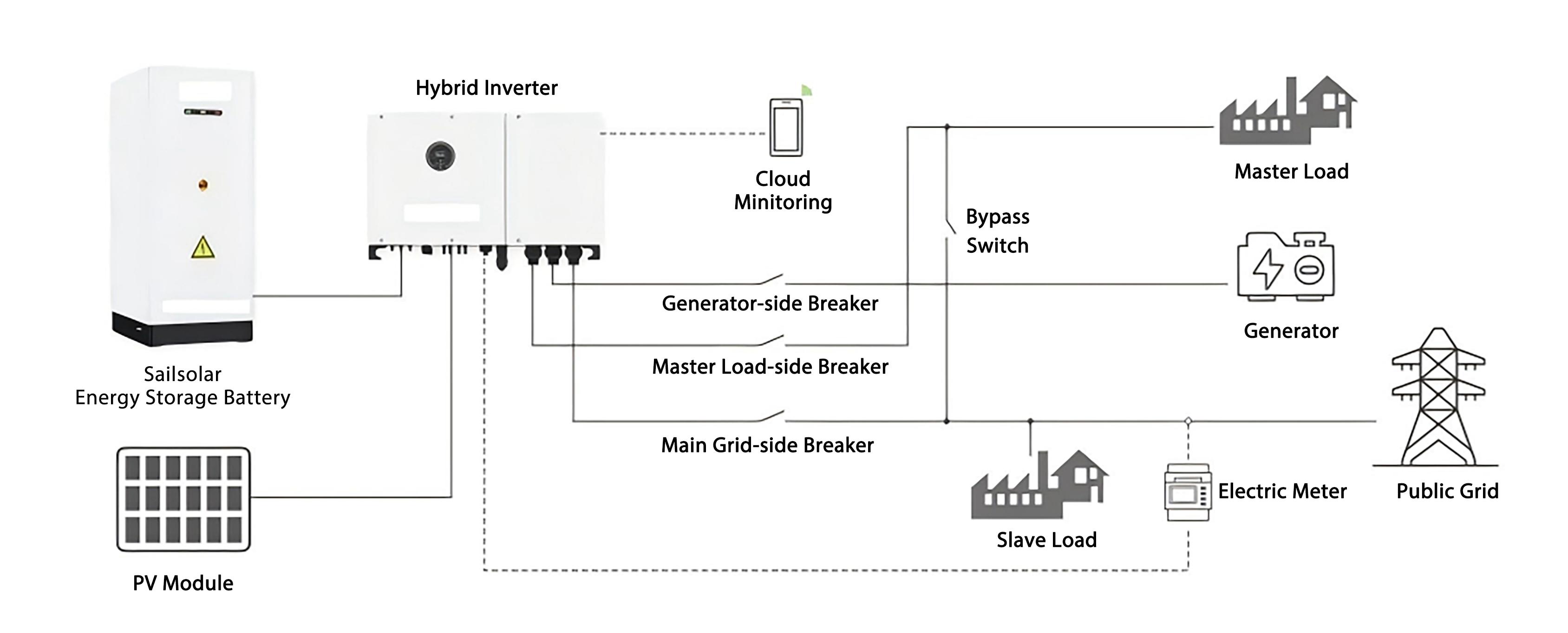
1. DC Coupling Architecture
In DC-coupled architecture, DC power from the PV array is stabilized by the DC-DC converter within a hybrid inverter (solar-storage inverter) and fed directly into the battery.
When power is needed, it can be drawn from either the PV array or the battery. In either case, the DC power is converted to AC by the DC-AC module within a hybrid inverter before being supplied to the loads.
Key Point: The energy remains entirely in DC form when charging the battery from the PV array, avoiding any lossy DC-AC-DC conversion.
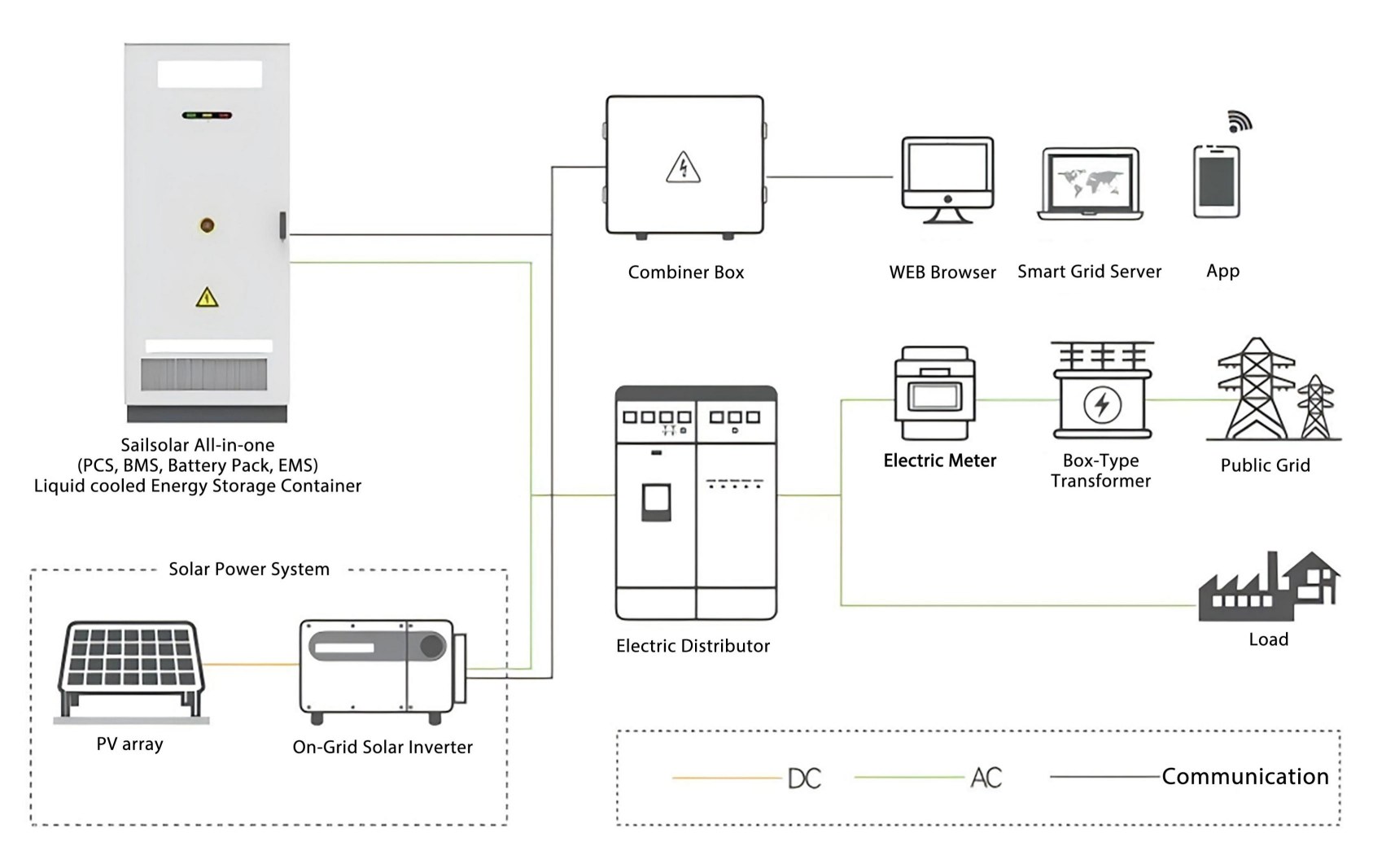
2. AC Coupling Architecture
In AC-coupled architecture, the PV and energy storage systems operate relatively independently. The DC power generated by the PV array is first converted to AC via a PV inverter, which then supplies the grid or local loads directly.
If AC power which convertered by solar inverter needs to be stored, it must be processed by a PCS (Power Conversion System), which converts it back to DC to charge the battery. When discharging, the PCS again converts the battery‘s DC power to AC for use by the loads.
Key Point: Charging the battery from the PV array requires a DC → AC → DC conversion process, and powering the loads adds a further DC → AC conversion.
3. Comparison for Both Architecture
(1) Energy Flow Path & Conversion Steps
DC Coupling: DC power generated by the PV modules can charge the battery directly (DC-DC), without undergoing DC-AC-DC conversion, resulting in lower energy losses.
AC Coupling: Storing PV power requires a two-step conversion (DC-AC-DC). When finally used, the power undergoes a total of three conversion steps, leading to relatively higher energy losses.
(2) System Equipment & Cost
DC Coupling: Utilizes an integrated hybrid inverter (or solar-storage inverter), which combines PV MPPT, bidirectional conversion, and battery management. This reduces the number of required components and interconnection cabling, lowering the initial investment. Fewer components also mean reduced installation and maintenance costs.
AC Coupling: Requires separate solar inverters and a battery inverter (PCS), along with a corresponding AC distribution board. The greater number of components increases cabling costs and requires more installation space.
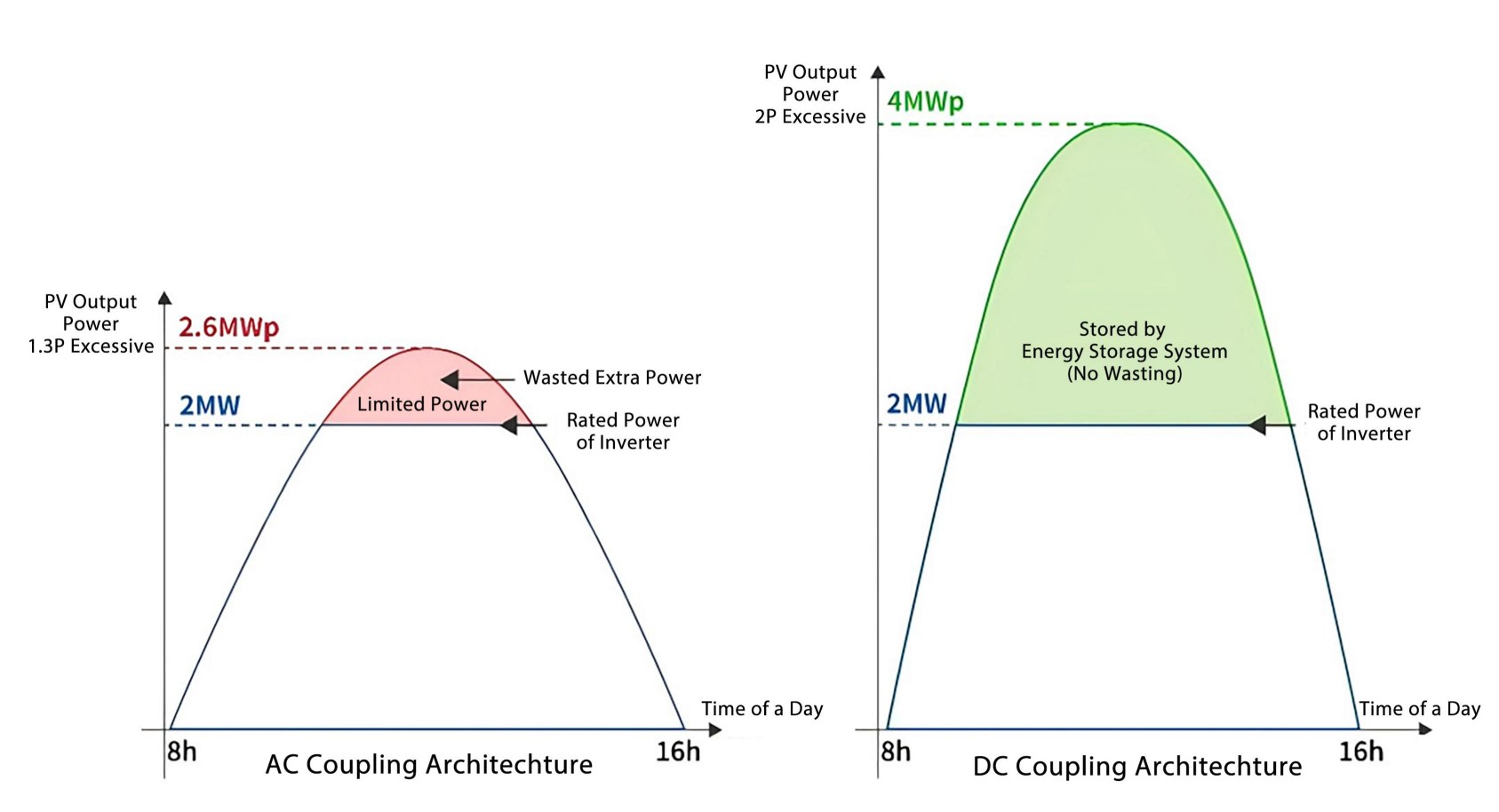
(3) DC-to-AC Ratio (Inverter Loading Ratio)
Assuming a factory transformer capacity of 2.5MVA, the total inverter output is typically limited to 80% of that capacity (approx. 2MW) for safe operation.
DC Coupling: Can support a 4MWp PV array. If the PV array generates 4MW of power, 2MW can flow directly to the battery for charging via the DC bus (a DC-DC process).
The remaining 2MW is converted by the PCS within the hybrid inverter and output as 2MW of AC power. The stored green energy can be dispatched during evening peak hours, maximizing the utilization of solar generation to meet higher corporate demand for renewable energy.
AC Coupling: PV generation is primarily limited by the PV inverter's capacity. With a 1.3 DC-to-AC ratio, a 2.6MWp PV array might be installed. If it generates 2.3MW DC, the 2MW AC PV inverter would constrain the output, causing the system to curtail PV generation and resulting in wasted solar energy.
(4) System Compatibility & Scalability
DC Coupling: Features high integration between the PV and storage systems. However, it has poor compatibility for retrofitting existing PV systems, often requiring replacement of the original inverter. System expansion is also constrained by the hybrid inverter's maximum input/output power and battery port specifications.
AC Coupling: Offers easy retrofitting for existing PV systems, as storage can be added by paralleling a battery inverter and batteries on the AC side. It allows flexible selection of equipment from different brands and provides stronger scalability.
4. How to Select AC&DC Coupling Solution
(1) DC Coupling:Scenarios such as new solar-storage system construction, pursuit of higher conversion efficiency and DC-to-AC ratio, and where installation space is somewhat limited.
(2) AC Coupling:Scenarios such as adding energy storage to existing PV systems, requiring compatibility with equipment from multiple brands, and hybrid integration of multiple energy sources.
Each method has its trade-offs, with no single optimal choice for all scenarios. The practical selection must be based on a comprehensive evaluation of the project's specific conditions and requirements. As both technologies continue to advance, they promise to deliver an ever-widening array of solutions, empowering users to make the optimal choice for their unique energy future.